Theme: Present and future advances in Genetics and Genetic Diseases
HUMAN GENETICS MEET 2024
We are excited to share the date of our forthcoming conference “12th International Conference on Human Genomics and Genomic Medicine”, which will be held during October 23-24, 2024 in Paris, France. This will explore the most cutting-edge research and development in human genetics. A number of outstanding researchers, scientists, industrialists, and others will be attending to showcase their groundbreaking work, share their experiences from various perspectives, and address important questions.
The scientific community has a venue to communicate knowledge in the area of human genetics and genetic diseases. Benefits professionals working in the fields of medicine, research, pharmacy, nursing, and other related fields who are interested in common health issues, this conference presents a thorough agenda given through plenary sessions and panel discussions.
Leading experts in the fields of genetic disease research, personalized and targeted medicine, as well as local and foreign professors, doctors, and government officials, will present sessions at this event.
Why to attend???
Human Genetics Meet 2024 cordially invites participants from all over the world to attend 12th International Conference on Human Genomics and Genomic Medicine, which is going to be held in Paris, France during October 23-24, 2024.
We invite you to meet us at the Human Genetics Meet 2024, where we will ensure that you’ll have a worthwhile experience with scholars of various branches including Genetics. By the generous response we received by our speakers, delegates, editorial board members from reputed journals and researchers from experience in the field of Genetics, we wish to make this conference successful in October 23-24, 2024.
We ensure that you will have a great session with renowned speakers in the field of Genetics and Genomic Medicine in the conference by bringing a group of experts to collaborate with our conference. Human Genomics and Genomic conference includes Oral presentations, Poster presentations, Workshops, Symposiums, Keynote presentations, Awards distribution for each category, and exhibition.
Target audience:
- Scientists
- R&D department people
- Students
- Professors
- Training Institutes
- Genetic engineers
- Bio-pharmacists
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Genomics and Pharmacogenomics Faculty
- CEO of Genetic companies
- Directors of Genetic companies
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Nutritionists
- Clinical protocol developers
- Geneticists
- Genetic Counselors
- Researchers
- Doctors
- Data Management Companies
- Enthusiastic people (common people, patients)
Why Dubai?
The first firm to provide complete genetic testing services in the Middle East is Eastern Biotech & Life Sciences, situated in Du Biotech, Dubai. In order to determine which genetic tests are most pertinent to this region and make them available to Middle Easterners directly, we have thoroughly investigated the biotechnological horizon.
ME Conferences chose the UAE to host its conference on "Human Genetics and Genetic Diseases" in order to enhance the participation of pioneer speakers in conference and make the attendees to explore, investigate, and exchange ideas on a worldwide scale.
Track 1: Human Genetics
Human Genetics is study for Analysis of the parent's progression of attributes. Human legacy in no crucial manner varies from that in different creatures. Human heredity research possesses a critical hereditary job. A lot of this interest gets from a profound longing to know who and why individuals are as they are. In a more reasonable manner, Understanding human legacy is basic in the expectation, analysis and treatment of hereditary infections. The journey to build up human wellbeing's hereditary premise has led to the clinical hereditary qualities industry. Medication has commonly given accentuation and reason to human hereditary qualities, so it is frequently viewed as exchangeable with the provisions of clinical hereditary qualities and human hereditary qualities.
- single-gene
- chromosomal
- multifactorial
Track 2: Evolutionary and Population Genetics
Developmental hereditary qualities are the wide field of studies that came about because of the reconciliation of hereditary qualities and Darwinian advancement, called the cutting edge blend. The power of change is a definitive wellspring of new hereditary variety inside populaces. Albeit most changes are unbiased with no impact on wellness or hurtful, a few transformations have a little, beneficial outcome on wellness and these variations are unrefined components for gradualist versatile development. Inside limited populaces, irregular hereditary float and regular determination influence the mutational variety. Regular choice is the main transformative power which can create variation, the fit among creature and climate, or ration hereditary states throughout extremely extensive stretches of time notwithstanding the dispersive powers of change and float.
Population genetics topics
- Mutation
- Genetic drift
- Natural selection
- Migration
Track 3: Bioinformatics, Machine learning and Statistical methods
Bioinformatics is both an umbrella term for the collection of organic investigations that utilization PC programming as a component of their technique, just as a source of perspective to explicit examination "pipelines" that are more than once utilized, especially in the field of genomics. Normal employments of bioinformatics incorporate the distinguishing proof of up-and-comer qualities and single nucleotide polymorphisms. Frequently, such distinguishing proof is made with the point of better understanding the hereditary sickness, interesting transformations, and helpful properties in rural species, or contrasts between populaces. In a less conventional manner, bioinformatics additionally attempts to comprehend the authoritative standards inside nucleic corrosive and protein successions, called proteomics
Statistical methods types
- Descriptive statistical analysis
- Inferential statistical analysis
- Associational statistical analysis
- Predictive analysis
- Prescriptive analysis
- Exploratory data analysis
- Causal analysis
Track 4: Gene Cloning and Mapping
DNA sequencing is the most common way of deciding the exact request of nucleotides inside a DNA particle. It incorporates any technique or innovation that is utilized to decide the request for the four bases is: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine, in a strand of DNA. The coming of quick DNA sequencing techniques has extraordinarily sped up natural and clinical exploration and disclosure. Information on DNA arrangements has become crucial for fundamental natural examination, and in various applied fields like clinical finding, biotechnology, scientific science, virology and Primate Systematics. The quick speed of sequencing achieved with current DNA sequencing innovation has been instrumental in the sequencing of complete DNA successions, or genomes of various kinds and types of life, including the human genome and other complete DNA groupings of numerous creature, plants, and microbial species
Types of cloning:
- Gene cloning
- Reproductive cloning
- Therapeutic cloning
Track 5: Cancer, Cardiovascular Diseases and Genetics
Hereditary sicknesses might be innate, passed down from the guardians qualities. In other hereditary sicknesses, deformities might be brought about by new transformations or changes to the DNA. All things considered, the deformity may be passed down assuming it happens in the microbe line. A similar illness, for example, a few types of disease might be brought about by an acquired hereditary condition in certain individuals, by new hereditary changes in others, and mostly by the natural causes in others. A hereditary infection is a hereditary issue brought about by at least one anomaly in the genome, particularly a condition that is available from birth intrinsic. Most hereditary illnesses are very uncommon and influence one individual in each few thousands or millions.
Track 6: Sickle cell Anaemia Genomics
Sickle-cell problem happens when somebody acquires two peculiar duplicates of the hemoglobin quality, one from each parent. This quality happens in chromosome eleven. A few subtypes exist, depending on the specific change in each hemoglobin quality. An attack might be actuating by utilizing temperature alterations, strain, drying out, and high height. A person with an unmarried unprecedented generation doesn't regularly have side effects and is expressed to have sickle-cell quality.
Track 7: Clinical Genetics and Novel Therapies of Genetic Diseases
Thalassemia is a hereditary issue which is caused because of unusual haemoglobin creation. Thalassemia is hereditary sickness acquired from an individual's father and mother. There are most significant sort, alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia. The seriousness of alpha and beta thalassemia depends upon on how among the four qualities for alpha globin or two qualities for beta globin is inadequate.
Track 8: Molecular Phenotyping and Omics Technologies
Molecular biology is the study of molecular underpinnings of the processes of replication, transcription, translation, and cell function. Molecular biology concerns the molecular basis of biological activity between the biomolecules in various systems of a cell, gene sequencing and this includes the interactions between the DNA, RNA and proteins and their biosynthesis. In molecular biology the researchers use specific techniques native to molecular biology, increasingly combine these techniques and ideas from the genetics and biochemistry.
Track 9: Mutation Detection and Analysis
In science, a change is the long-lasting adjustment of the nucleotide arrangement of the genome of a creature, infection, or extra chromosomal DNA or other hereditary components. Transformations result from blunders during DNA replication or different kinds of harm to DNA, which then, at that point, may go through mistake inclined fix or cause a mistake during different types of fix, or, more than likely may cause a blunder during replication interpretation amalgamation. Changes may likewise result from addition or erasure of portions of DNA because of versatile hereditary components. Transformations might create recognizable changes in the perceptible qualities aggregate of a living being. Transformations have an influence in both ordinary and unusual organic cycles including: advancement, disease, and the improvement of the invulnerable framework, including utilitarian variety. The genomes of RNA infections depend on RNA rather than DNA. The RNA viral genome can be twofold abandoned DNA or single abandoned. In a portion of these infections, for example, the single abandoned human immunodeficiency infection replication happens rapidly and there are no components to really look at the genome for precision.
Track 10: Molecular and Cytogenetics
Molecular genetics is the sector of biology that researches the structure and characteristic of genes at a molecular stage and hence employs strategies of each molecular biology and genetics. The study of chromosomes and gene expression of an organism can give insight into heredity, genetic variant, and mutations. This is useful in the observe of Developmental Biology and in expertise and treating genetic illnesses.
Track 11: Molecular Effects of Genetic Variation
Molecular modeling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behavior of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems
Track 12: Functional Genomics and Transcriptomics
Immunogenetics is the part of clinical examination that investigates the connection between the safe framework and hereditary qualities. Immune system illnesses, like sort diabetes, are complicated hereditary attributes which result from surrenders in the insusceptible framework. Distinguishing proof of qualities characterizing the insusceptible imperfections might recognize new objective qualities for remedial methodologies. Then again, hereditary varieties can likewise assist with characterizing the immunological pathway prompting sickness.
Track 13: Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenetics is the investigation of microbe line transformations, the single-nucleotide polymorphisms influencing qualities coding for liver proteins liable for drug testimony and pharmacokinetics, though pharmacogenomics alludes to physical changes in tumoral DNA prompting modification in drug reaction KRAS changes in patients treated with hostile to Her1 biologics. Pharmacogenetics is an acquired hereditary contrast in drug metabolic pathways which can influence individual reactions to drugs, both as far as helpful impact just as antagonistic impacts. The term Pharmacogenetics is frequently utilized reciprocally with the term pharmacogenomics which additionally explores the job of gained and acquired hereditary contrasts according to medicate reaction and medication conduct through a precise assessment of qualities, quality items, and between and intra-individual variety in quality articulation and capacity.
Track 14: Epigenetics and Gene Regulation
Epigenetics are stable heritable traits that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. Epigenetics often refers to changes in a chromosome that affect gene activity and expression, but can also be used to describe any heritable phenotypic change that does not derive from a modification of the genome, such as prions. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal developmental program. Gene expression can be controlled through the action of repressor proteins that attach to silencer regions of the DNA. These epigenetic changes may last through cell divisions for the duration of the cell's life, and may also last for multiple generations even though they do not involve changes in the underlying DNA sequence of the organism; instead, non-genetic factors cause the organism's genes to behave or "express themselves" differently.
Three classes of epigenetic regulation exist:
- DNA methylation,
- Histone modification
- Noncoding RNA
Track 15: Stem cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic foundational microorganism transplantation is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic undeveloped cells, typically got from bone marrow, fringe blood, or umbilical string blood. It could be autologous the patient's own immature microorganisms are utilized, allogeneic the undeveloped cells come from a giver or syngeneic from an indistinguishable twin. It is an operation in the area of hematology, most frequently performed for patients with specific malignant growths of the blood or bone marrow, like different myeloma or leukemia. In these cases, the beneficiary's resistant framework is generally obliterated with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Contamination and unite versus-have illness are significant complexities of allogeneic.
Hematopoietic undifferentiated cell transplantation stays a hazardous system with numerous potential entanglements; it is saved for patients with dangerous sicknesses. As endurance following the system has expanded, its utilization has extended past malignant growth, like immune system sicknesses and inherited skeletal dysplasia's quite dangerous puerile osteoporosis and mucopolysaccharidosis.
Types of Stem Cell Transplantation
- Autologous stem cell transplant
- Allogeneic stem cell transplant
Track 16: Translational Medicine
Translational medication is a quickly developing discipline in biomedical examination and plans to speed up the disclosure of new indicative devices and therapies by utilizing a multi-disciplinary, profoundly cooperative; "seat to-bedside" approach. Inside general wellbeing, translational medication is centred on guaranteeing that demonstrated techniques for illness treatment and counteraction are really executed inside the local area. One predominant depiction of translational medication, first presented by the Institute of Medicine's Clinical Research Roundtable, features two barricades that is unmistakable regions needing improvement the primary translational square (T1) keeps fundamental examination discoveries from being tried in a clinical setting; the second translational square (T2) keeps demonstrated mediations from becoming standard practice. The National Centre for Advancing Translational Science (NCATS) was set up inside the NIH to "change the translational science process with the goal that new medicines and remedies for illness can be conveyed to patients quicker.
Track 17: Genetic Biotechnology and Genetic Microbiology
Genetic biotechnology involves the manipulation of genes and genetic material to develop products and processes with practical applications in various industries, including medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. Genetic microbiology focuses specifically on the study of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protists, using genetic and molecular biology techniques. This field encompasses various areas of research.
Key aspects of genetic biotechnology include:
- Gene Cloning and Recombinant DNA Technology
- Gene Editing and Genome Engineering
- Synthetic Biology
- Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis
- Microbial Genetics
- Microbial Genomics
- Molecular Epidemiology
The Human Genetics request assiduity is projected to grow from USD28.69 Billion in 2023 to USD65.18 Billion by 2032, flaunting a composite periodic growth rate (CAGR) of10.80 during the cast period (2023-2032). Growing demand for individualized drugs, rising research conditioning in genomics, increasing investments in genomics and inheritable testing companies, rising frequency of inheritable diseases, advances in genomic technologies, are the crucial requests motorists enhancing the request growth.
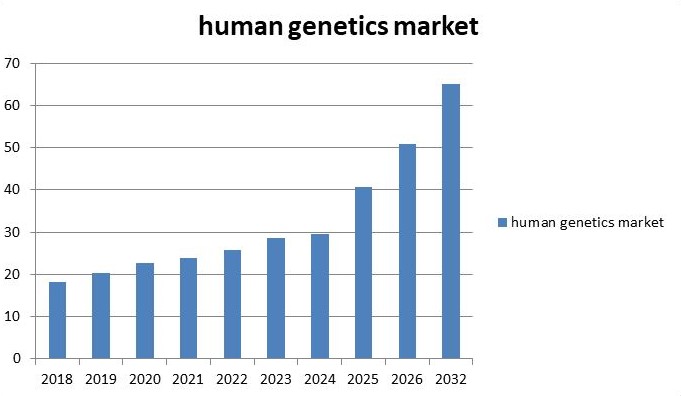
Using genomic tools in remedial settings has also altered mortal genetics as a scientific discipline. Further people now have access to further affordable inheritable testing, allowing for earlier and more accurate opinions of heritable conditions. Inheritable information is now being used to guide treatment opinions, point causes of complaint, and determine the most effective specifics and dosing schedules for individual cases. The arrival of individualized drugs, in which care is acclimatized to an existent's inheritable makeup, is made possible by these technological advancements. Hence, fueling profitable growth in the Human genetics industry. There are only a sprinkle of places where mortal genetics has been put to use so far. On the other hand, prosperous expansion is anticipated in the times to come. With the help of computational biology, we'll have a plenitude of room to keep track of all the inheritable data we collect from people around the world. Similarly, as mortal genetics finds further and further uses in molecular individual testing, request players may anticipate seeing a sizable increase in income. The need for gene remedy is rising fleetly because of the intimidating rise in the prevalence of inheritable ails around the world. To respond, scientists in R&D and forensics labs are digging deep into mortal DNA to discover new, more effective treatments for a wide range of ails. The design has the backing of governments around the world, which are spending considerably in the mortal genetics assiduity to raise public knowledge of inheritable ails, available curatives, and their impact on diurnal life.
The 12th International Conference on Human Genomics and Genomic Medicine was held on March 28-29, 2024 at Dubai, UAE. The conference brought together experts from different fields to discuss and share their knowledge on in Human Genetics and Genetic Diseases.
The presentations were made by experts from academia, industry, and government organizations. Some of the topics covered in the presentations included Human Genetics, Genetics, Genetic Diseases and further.
In addition to the presentations, there were also panel discussions and Q&A sessions where participants engaged in lively discussions on various topics. The conference also provided ample opportunities for networking, which allowed participants to exchange ideas and establish new collaborations.
Overall, the “12th International Conference on Human Genomics and Genomic Medicine” was a great success, and it provided a platform for experts from different fields to come together and discuss the latest research and developments in Genetics. The conference was informative, engaging, and offered excellent networking opportunities. We look forward to attending the next edition of this conference that is “11th World Congress on Human Genetics and Genetic Diseases” which is to be held in July 10-11, 2023 at Dubai, UAE.
Conference Highlights
- Human Genetics
- Evolutionary and Population Genetics
- Bioinformatics, Machine learning and Statistical methods
- Gene Cloning and Mapping
- Cancer, Cardiovascular Diseases and Genetics
- Sickle cell Anaemia Genomics
- Clinical Genetics and Novel Therapies of Genetic Diseases
- Molecular Phenotyping and Omics Technologies
- Mutation Detection and Analysis
- Molecular and Cytogenetics
- Molecular Effects of Genetic Variation
- Functional Genomics and Transcriptomics
- Pharmacogenomics
- Epigenetics and Gene Regulation
- Stem cell Transplantation
- Translational Medicine
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 23-24, 2024 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Molecular and Genetic Medicine
- Human Genetics & Embryology
- Journal of Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



